© All rights reserved galwayclinic.com 2013

What are the types of arrhythmias?
• Tachycardia: A fast heart rhythm with a rate of more than 100 beats per minute. • Bradycardia: A slow heart rhythm with a rate below 60 beats per minute. • Supraventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the atria (the heart’s upper chambers). • Ventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the ventricles (the heart’s lower chambers. • Bradyarrhythmias: Slow heart rhythms that may be caused by disease in the heart’s conduction system, such as the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node or HIS-Purkinje network .
Arrhythmias can be caused by:
• Abnormal extra electrical circuits in the heart • Increased electrical activity of a single focus of heart muscle • Scar tissue in the heart from a prior heart attack • Abnormal electrical firing of the pulmonary veins • High blood pressure • Changes in the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy) • Valve disorders • Electrolyte imbalances in the blood, such as sodium or potassium • Injury from a prior heart attack with scar formation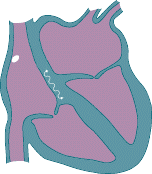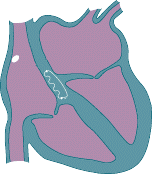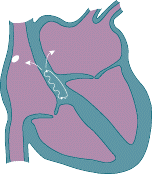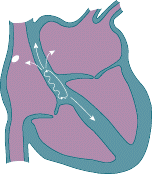
Galway Clinic Facebook page
Tel: +353 (0) 91720170 brendan.ocochlain@galwayclinic.com





Galway Site Design

What are the types of arrhythmias?
• Tachycardia: A fast heart rhythm with a rate of more than 100 beats per minute. • Bradycardia: A slow heart rhythm with a rate below 60 beats per minute. • Supraventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the atria (the heart’s upper chambers). • Ventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the ventricles (the heart’s lower chambers. • Bradyarrhythmias: Slow heart rhythms that may be caused by disease in the heart’s conduction system, such as the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node or HIS- Purkinje network .
Arrhythmias can be caused by:
• Abnormal extra electrical circuits in the heart • Increased electrical activity of a single focus of heart muscle • Scar tissue in the heart from a prior heart attack • Abnormal electrical firing of the pulmonary veins • High blood pressure • Changes in the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy) • Valve disorders • Electrolyte imbalances in the blood, such as sodium or potassium • Injury from a prior heart attack with scar formation

Galway Clinic Facebook page